__ __ ___ _____ _____
\ \ / / / _ \ | ___ \ | ___ \
\ V / / /_\ \ | |_/ / | |_/ /
\ / | _ | | __/ | __/
| | | | | | | | | |
\_/et \_| |_/nother \_|hasing \_|rogram
Overview
yapp is a program that includes a set of utilities to work on high
density genetic data in pedigrees.
yapp and its utilities implement some models and methods that have been invented by other people. If you use yapp it is important that you acknowledge their work by citing the appropriate references. These will depend on the way you use the software. The documentation below provides the relevant citations.
Installation
yapp has been tested to work on Linux and MacOSX with python
versions >= 3.7. It is suggested to install yapp within a
python virtual
environment.
Briefly this is done with these commands:
python -m venv yappenv
cd yappenv
source bin/activate
## make sure a recent version of pip is installed
pip install -U pip
Then, install Numberjack from github. First checkout that you have installed the required dependencies:
- python-dev
- swig (3.X)
- libxml2-dev
- zlib1g-dev
- libgmp-dev
Then install it using the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/eomahony/Numberjack.git
cd Numberjack
python setup.py build
pip install .
Finally, you can install yapp (note that the python package name is yappgen):
pip install yappgen
To run some of yapp utilities on a computer cluster you can additionally install ray (pip install ray)
Usage
yapp has a command line interface that is used to launch different
commands. Type yapp -h for detailed help. The basic syntax is :
yapp <command> <args1, args2, ..., argsN>
Most commands take as input files a VCF file, its
index obtained with tabix, and a FAM
file with family
information. yapp writes logs of all commands to a common log file ending in _yapp.log.
This way all steps of an analysis will be logged in the same place (the file is not overwritten).
yapp commands try to use multiple processors when required. By default they will use all that are
available. To control this number use the -c option.
Workflow of yapp commands
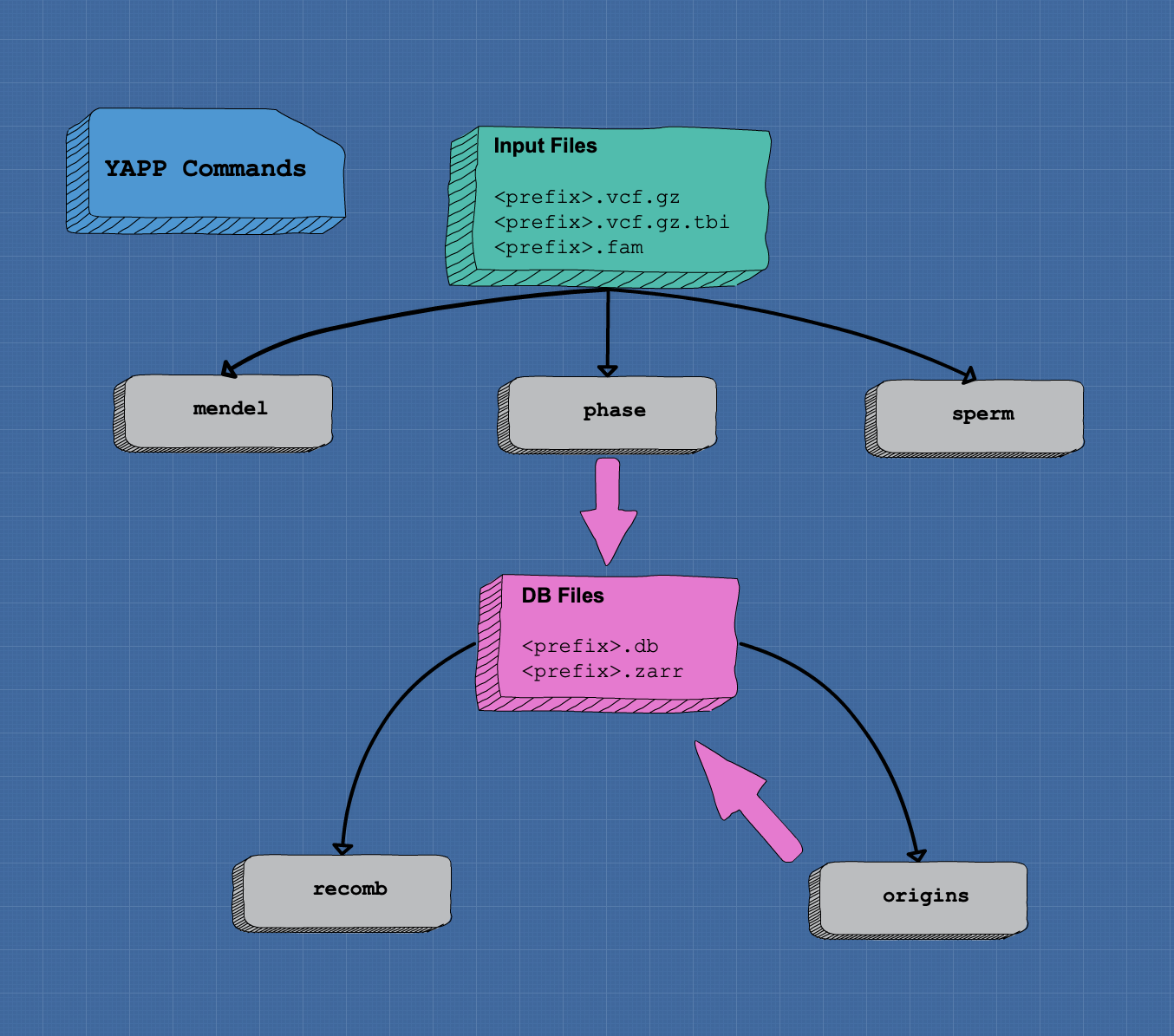
Available commands are:
mendel
yapp mendel <prfx>
This command performs checks for Mendelian errors between all parent -> offspring pairs. It will identify pairs that exhibit a large number of such errors and are therefore likely to be pedigree errors. It produces a new FAM file where such errors have been removed and that can be used in subsequent analyses.
phase
The phase command is used to infer gametic phase and segregation
indicators in a genotyped pedigree. The usage is:
yapp phase <prfx>
where prfx is the prefix of all input files :
<path/to/prefix>.fam , <path/to/prefix>.vcf.gz ,
<path/to/prefix>vcf.gz.tbi. Note that when exporting a plink bed
file to VCF, you must do so using --recode vcf-iid so that sample
names in the resulting VCF do no include the family-ID.
The output files produced are a phased VCF <path/to/prefix>_phased.vcf.gz and a
binary file <path/to/prefix>_yapp.db. This binary file is useful
for conducting analyses with other yapp commands. yapp also stores
the data on disk in the form of zarr Zarrays which makes it
convenient to work with and transfer information from one yapp
command to another or if you want to access programatically (in
python) the results. When you are finished using it you might consider
deleting those files as they can be big.
Citation
yapp phase uses a Weighted Constraints Satisfaction Problem solver,
ToulBar2, to infer parental phase
from transmitted gametes. This idea was developped by Aurélie Favier
during her PhD with Simon de Givry and Andres Legarra.
recomb
The recomb command is used to detect crossing overs from phased
data. It is meant to be run after a yapp phase run. It will produce
two output files <path/to/prefix>_yapp_recombinations.txt with the
localization of detected crossing over events and
<path/to/prefix>_yapp_recomb_coverage.txt that provides for each
meiosis (parent -> offspring) and each chromosome the interval within
which crossing overs can be detected.
origins
only available for version > 0.1
The origins command is used to trace down transmission of ancestral
alleles in the pedigree. Any chromosome of unknown ancestral origin is
given a unique identifier that is then followed through segregations
from parent to offspring.
This command :
- creates a new
linkagegroup in the zarr archive with origins - produces new output files:
<path/to/prefix>_yapp_ancestors.txt: correspondance between ancestors and ancestral allele codes<path/to/prefix>_ancestral_props.txt: for each individual gives the proportion of SNPs inherited from each ancestral allele<path/to/prefix>_pedGRM.txt: gives the estimated kinship coefficients for each pair of individuals in the pedigree. It is a genomic relationship matrix (GRM) based on linkage data.
sperm
The sperm command is used to infer parental genotype and phases from
genotyping data of its gametes. The input files are the same as for
the phase command with additional requirements :
1. the fam file should not contain pedigree information (columns 3 and
4 are ignored) but use the FID (/i.e./ first) column to relate an
individual to its gametes
2. the vcf file will be read assuming individuals are completely
inbred (haploid gametes). Any heterozygote genotype is treated as
missing.
An output file is created for each gamete set found in the input files
(/i.e./ each unique identifier in the FID column of the fam
file). This file is in tped format with the additional information that
haplotypes are phased. If you read it with plink the phase info will
probably disappear.
Other Utilities
fphtrain
fphtrain trains a fastphase model on a set of individuals. It takes
as input a vcf_file (gzipped and indexed) and a number of haplotype
clusters. Genotype data can be read assuming different modes:
- genotype : unphased diploids
- phased : phased diploids. The phase information is taken from the VCF file (| sign). Unphased genotype are treated as missing.
- inbred : completely homozygous genotypes, treated as haploids. Heterozygote genotypes are treated as missing.
- likelihood : used the GL field from the VCF corresponding to the likelihood of each genotype on a PHRED scale (-10*log10(lik)).
Citation
If you use the likelihood mode, cite:
© Bertrand Servin 2021